No Preview Available !

The 555 Timer IC
(Adapted from http://www.electronics.dit.ie/staff/mtully/555%20folder/555%20timer.htm)
The 555 timer IC was first introduced around 1971 by the Signetics Corporation as the SE555/NE555 and was
called "The IC Time Machine" and was also the very first and only commercial timer IC available. It provided circuit
designers with a relatively cheap, stable, and user-friendly integrated circuit for both monostable and astable
applications. Since this device was first made commercially available, a myriad of novel and unique circuits have
been developed and presented in several trade, professional, and hobby publications. The past ten years some
manufacturers stopped making these timers because of competition or other reasons. Yet other companies, like
NTE (a subdivision of Philips) picked up where some left off.
Although these days the CMOS version of this IC, like the Motorola MC1455, is mostly used, the regular type is
still available, however there have been many improvements and variations in the circuitry. But all types are pin-for-
pin plug compatible.
In this tutorial the 555 timer is examined in detail along with its uses, either by itself or in combination with other
solid state devices. This timer uses a maze of transistors, diodes and resistors and for this complex reason a more
simplified (but accurate) block diagram is used to
explain the internal organizations of the 555.
The 555, in fig. 1 and fig. 2 above, comes in
two packages, either the round metal-can called
the 'T' package or the more familiar 8-pin DIP 'V'
package. About 20-years ago the metal-can type
was pretty much the standard (SE/NE types). The
556 timer is a dual 555 version and comes in a
14-pin DIP package, the 558 is a quad version
with four 555's also in a 14 pin DIP case.
Inside the 555 timer, at fig. 3, are the
equivalent of over 20 transistors, 15 resistors, and
2 diodes, depending of the manufacturer. The
equivalent circuit, in block diagram, providing the
functions of control, triggering, level sensing or
comparison, discharge, and power output. Some
of the more attractive features of the 555 timer
are: Supply voltage between 4.5 and 18 volt,
supply current 3 to 6 mA, and a Rise/Fall time of
100 nSec. It can also withstand quite a bit of
abuse. The Threshold current determine the
maximum value of Ra + Rb. For 15 volt operation
the maximum total resistance for R (Ra +Rb) is 20
MΩ.
The supply current, when the output is 'high', is typically 1 milli-amp (mA) or less. The initial monostable timing
accuracy is typically within 1% of its calculated value, and exhibits negligible (0.1%/V) drift with supply voltage.
Thus long-term supply variations can be ignored, and the temperature variation is only 50ppm/°C (0.005%/°C).
All IC timers rely upon an external capacitor to determine the off-on time intervals of the output pulses. It takes
a finite period of time for a capacitor (C) to charge or discharge through a resistor (R). Those times are clearly
defined and can be calculated given the values of resistance and capacitance.
1 page

The capacitor slows down as it charges, and in actual fact never reaches the full supply voltage. That being the
case, the maximum charge it receives in the timing circuit (66.6% of the supply voltage) is a little over the charge
received after a time constant (63.2%).
The capacitor slows down as it discharges, and never quite reaches the ground potential. That means the
minimum voltage it operates at must be greater than zero. Timing circuit is 63.2% of the supply voltage.
The discharge of a capacitor also takes time and we can shorten the amount of time by decreasing resistance
(R) to the flow of current.
Operating Modes: The 555 timer has two basic operational modes: one shot and astable. In the one-shot
mode, the 555 acts like a monostable multivibrator. A monostable is said to have a single stable state--that is the
off state. Whenever it is triggered by an input pulse, the monostable
switches to its temporary state. It remains in that state for a period of time
determined by an RC network. It then returns to its stable state. In other
words, the monostable circuit generates a single pulse of a fixed time
duration each time it receives and input trigger pulse. Thus the name one-
shot. One-shot multivibrators are used for turning some circuit or external
component on or off for a specific length of time. It is also used to
generate delays. When multiple one-shots are cascaded, a variety of
sequential timing pulses can be generated. Those pulses will allow you to
time and sequence a number of related operations.
The other basic operational mode of the 555 is as and astable
multivibrator. An astable multivibrator is simply and oscillator. The astable multivibrator generates a continuous
stream of rectangular off-on pulses that switch between two voltage levels. The frequency of the pulses and their
duty cycle are dependent upon the RC network values.
One-Shot Operation: Fig. 4 shows the basic circuit of the 555 connected as a monostable multivibrator. An
external RC network is connected between the supply voltage and ground. The junction of the resistor and
capacitor is connected to the threshold input which is the input to the upper comparator. The internal discharge
transistor is also connected to the junction of the resistor and the capacitor. An input trigger pulse is applied to the
trigger input, which is the input to the lower comparator.
With that circuit configuration, the control flip-flop is initially reset. Therefore, the output voltage is near zero volts.
The signal from the control flip-flop causes T1 to conduct and act as a short circuit across the external capacitor.
For that reason, the capacitor cannot charge. During that time, the input to the upper comparator is near zero volts
causing the comparator output to keep the control flip-flop reset.
Notice how the monostable continues to output its pulse regardless of the inputs swing back up. That is
because the output is only triggered by the input pulse, the output actually depends on the capacitor charge.
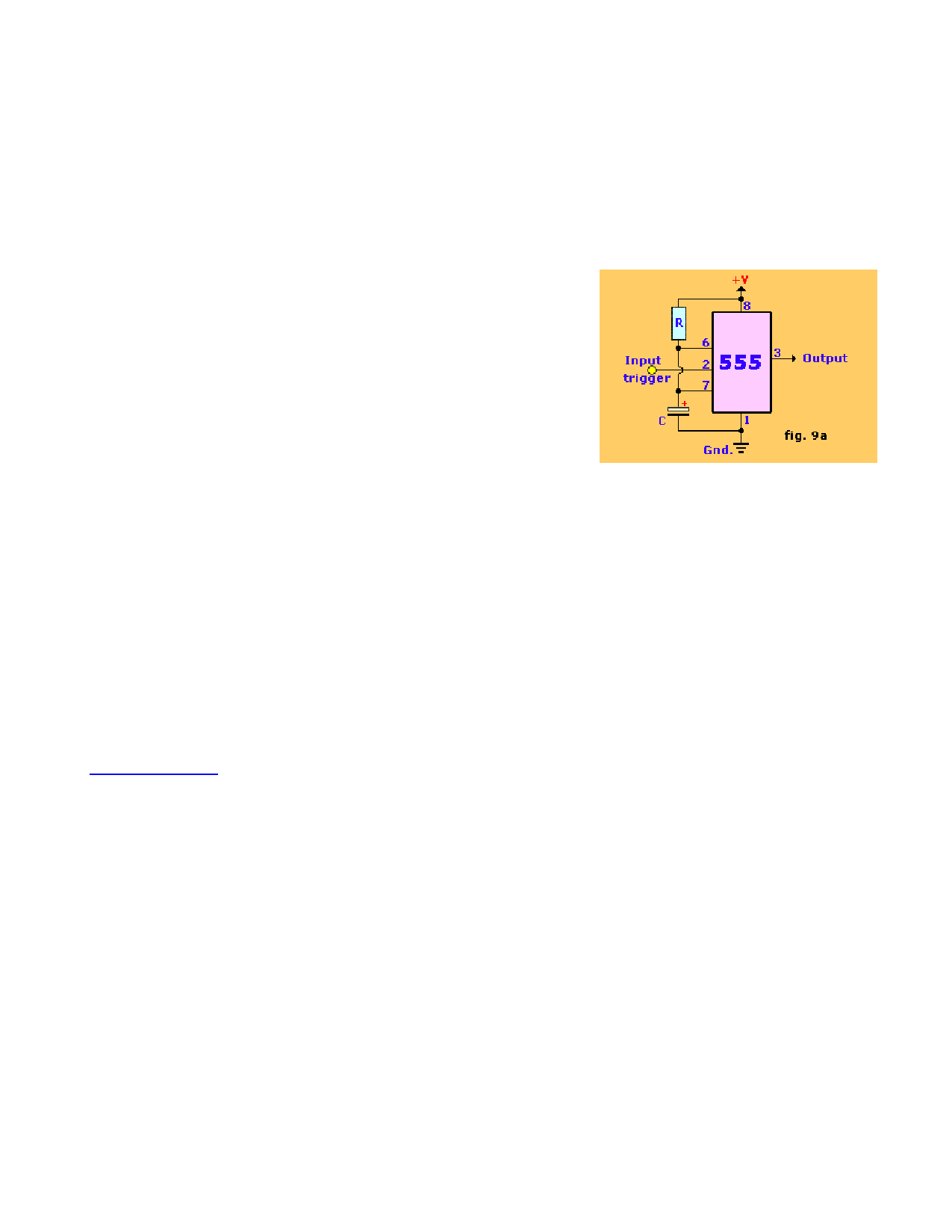
Monostable Mode:
The 555 in fig. 9a is shown here in it's utmost basic mode of operation; as a triggered monostable. One
immediate observation is the extreme simplicity of this circuit. Only two components to make up a timer, a capacitor
and a resistor. And for noise immunity maybe a capacitor on pin 5. Due to the internal latching mechanism of the
555, the timer will always time-out once triggered, regardless of any subsequent noise (such as bounce) on the
input trigger (pin 2). This is a great asset in interfacing the 555 with noisy sources. Just in case you don't know what
'bounce' is: bounce is a type of fast, short term noise caused by a switch, relay, etc. and then picked up by the input
pin.
The trigger input is initially high (about 1/3 of +V). When a negative-going trigger pulse is applied to the trigger
input (see fig. 9a), the threshold on the lower comparator is exceeded. The lower comparator, therefore, sets the
flip-flop. That causes T1 to cut off, acting as an open circuit. The setting of the flip-flop also causes a positive-going
output level which is the beginning of the output timing pulse.
The capacitor now begins to charge through the external resistor. As soon as the charge on the capacitor equal
2/3 of the supply voltage, the upper comparator triggers and resets the control flip-flop. That terminates the output
pulse which switches back to zero. At this time, T1 again conducts thereby discharging the capacitor. If a negative-
going pulse is applied to the reset input while the output pulse is high, it will be terminated immediately as that
pulse will reset the flip-flop.
Whenever a trigger pulse is applied to the input, the 555 will generate its single-duration output pulse.
Depending upon the values of external resistance and capacitance used, the output timing pulse may be adjusted
from approximately one millisecond to as high as on hundred seconds. For time intervals less than approximately
1-millisecond, it is recommended that standard logic one-shots designed for narrow pulses be used instead of a
5 Page

Circuits 11 to 14:
Play with different indicating devices such as bells, horns, lights, relays, or whatever (if possible). Try different types
of LDR's. If for any reason you get false triggering, connect a ceramic 0.01uF (=10nF) capacitor between pin 5
(555) and ground. In all circuit diagrams below I used the LM555CN timer IC from National. The 555 timer will work
with any voltage between 3.5 and 15volt. A 9-volt battery is usually a general choice. Keeping notes is an important
aspect of the learning process.
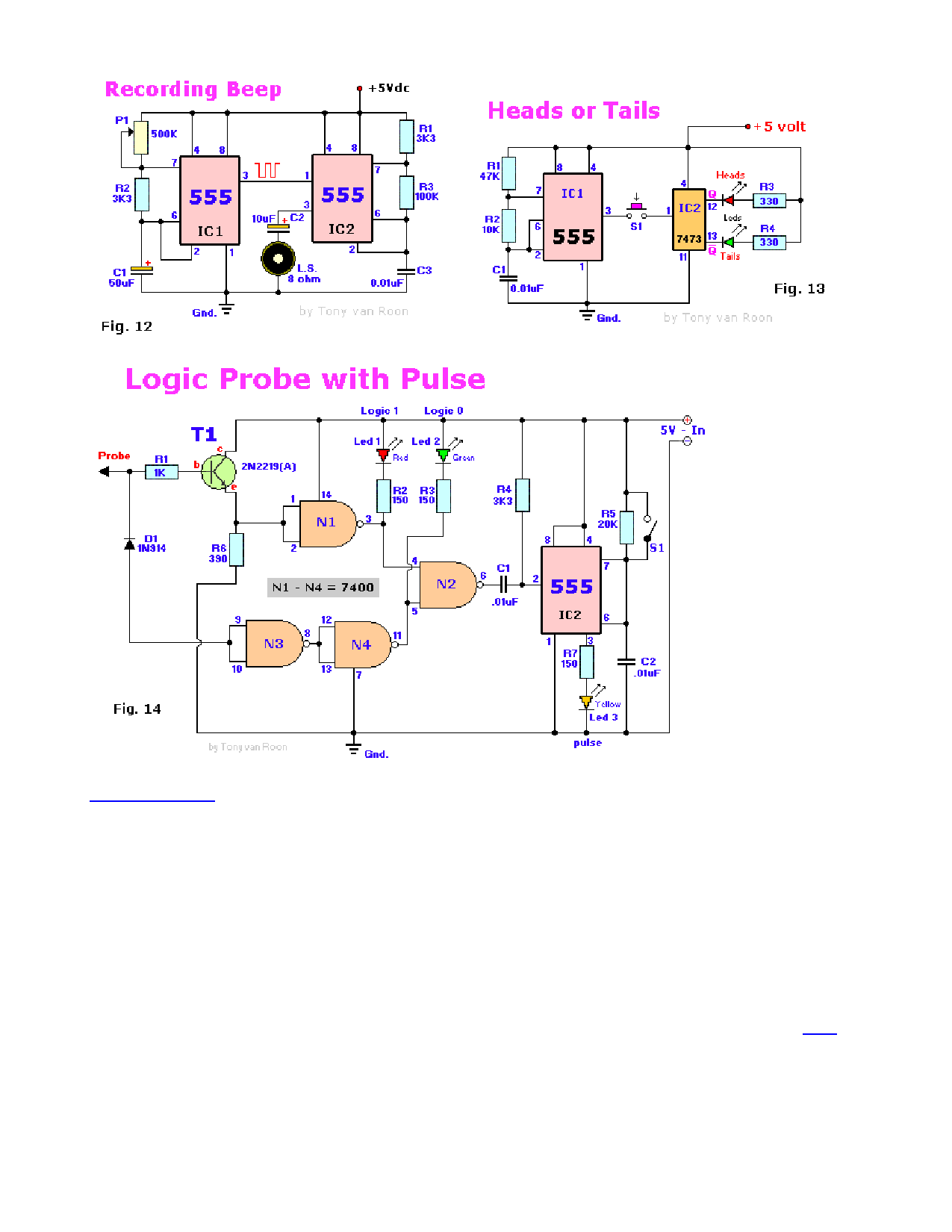
Fig. 11, Two-Tones: The purpose of this experiment is to wire two 555 timers together to create a 2-note tone. If
you wish, you can use the dual 556 timer ic.
Fig. 12, Recording Beep: This circuit is used to keep recording of telephone conversations legal. As you may
know, doing otherwise without consent of the other party is illegal. The output of IC1 is fed to the 2nd 555's pin 3
and made audible via C2 and the speaker. Any 8-ohm speaker will do.
Fig. 13, Coin Toss: Electronic 'Heads-or-tails' coin toss circuit. Basically a Yes or No decision maker when you
can't make up your mind yourself. The 555 is wired as a Astable Oscillator, driving in turn, via pin 3, the 7473 flip-
flop. When you press S1 it randomly selects the 'Heads' or 'Tails' led. The leds flash rate is about 2Khz (kilo-Hertz),
which is much faster than your eyes can follow, so initially it appears that both leds are 'ON'. As soon as the switch
is released only one led will be lit.
Fig. 14, Logic Probe: Provides you with three visible indicators; "Logic 1" (+, red led), "Logic 0" (-, green led), and
"Pulse" (yellow led). Good for TTL and CMOS. The yellow or 'pulse' led comes on for approximately 200 mSec to
indicate a pulse without regards to its width. This feature enables one to observe a short-duration pulse that would
11 Page
|