
|
|
PDF ISL62875 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | ISL62875 | |
| Descripción | PWM DC/DC Controller | |
| Fabricantes | Intersil | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de ISL62875 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 22 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
c1No-8nO8ta8Rc-IEtNCoOTuOEBrMRSTSMOeIcELLhENonTDriEcEwaDPwl RSRwOuE.ipDnPptULeoACrrstCTiClE.ceMonEmteN/rtTsact
PWM DC/DC Controller with VID Inputs for
Portable GPU Core-Voltage Regulator
ISL62875
The ISL62875 is a Single-Phase Synchronous-Buck
PWM voltage regulator featuring Intersil’s Robust Ripple
Regulator (R3) Technology™. The wide 3.3V to 25V
input voltage range is ideal for systems that run on
battery or AC-adapter power sources. The ISL62875 is a
low-cost solution for applications requiring dynamically
selected slew-rate controlled output voltages. The
soft-start and dynamic setpoint slew-rates are capacitor
programmed. Voltage identification logic-inputs select
four resistor-programmed setpoint reference voltages
that directly set the output voltage of the converter
between 0.5V to 1.5V, and up to 3.3V using a feedback
voltage divider. Robust integrated MOSFET drivers and
Schottky bootstrap diode reduce the implementation
area and component cost.
Intersil’s R3 Technology™ combines the best features of
both fixed-frequency and hysteretic PWM control. The
PWM frequency is 500kHz during static operation,
becoming variable during changes in load, setpoint
voltage, and input voltage when changing between
battery and AC-adapter power. The modulators ability to
change the PWM switching frequency during these
events in conjunction with external loop compensation
produces superior transient response. For maximum
efficiency, the converter automatically enters diode-
emulation mode (DEM) during light-load conditions such
as system standby.
Features
• Input Voltage Range: 3.3V to 25V
• Output Voltage Range: 0.5V to 3.3V
• Output Load up to 30A
• Extremely Flexible Output Voltage Programmability
- 2-Bit VID Selects Four Independent Setpoint
Voltages
- Simple Resistor Programming of Setpoint Voltages
- Accepts External Setpoint Reference such as DAC
• ±0.75% System Accuracy: -10°C to +100°C
• Fixed 500kHz PWM Frequency in Continuous
Conduction
• Integrated High-current MOSFET Drivers and
Schottky Boot-Strap Diode for Optimal Efficiency
Applications*(see page 21)
• Mobile PC GPU Core Power
• Mobile PC I/O Controller Hub (ICH) VCC Rail
• Tablet PCs/Slates and Netbooks
• Hand-Held Portable Instruments
Related Literature*(see page 21)
• TB389 “PCB Land Pattern Design and Surface Mount
Guidelines for QFN Packages”
Typical Application
+5V
GPIO
CPVCC
1
2
PGND
3
GND
4
EN
5 VID1
6 VID0
7 SREF
8 SET0
9 SET1
20
19
VCC
18
BOOT
17
UGATE
PHASE 16
14
OCSET
13
VO
12
FB
10 11 VCC
RSET1 RSET2 RSET3
GPIO
CVCC
QHS
CBOOT
QLS
VIN
3.3V TO 25V
CIN
LO
COCSET
VOUT
0.5V TO 3.3V
COUT
RCOMP
CCOMP
RO
RFB
FN6905.1
September 18, 2009
1
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774 | Intersil (and design) is a trademark of Intersil Americas LLC
Copyright Intersil Americas LLC 2009. All Rights Reserved
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
1 page 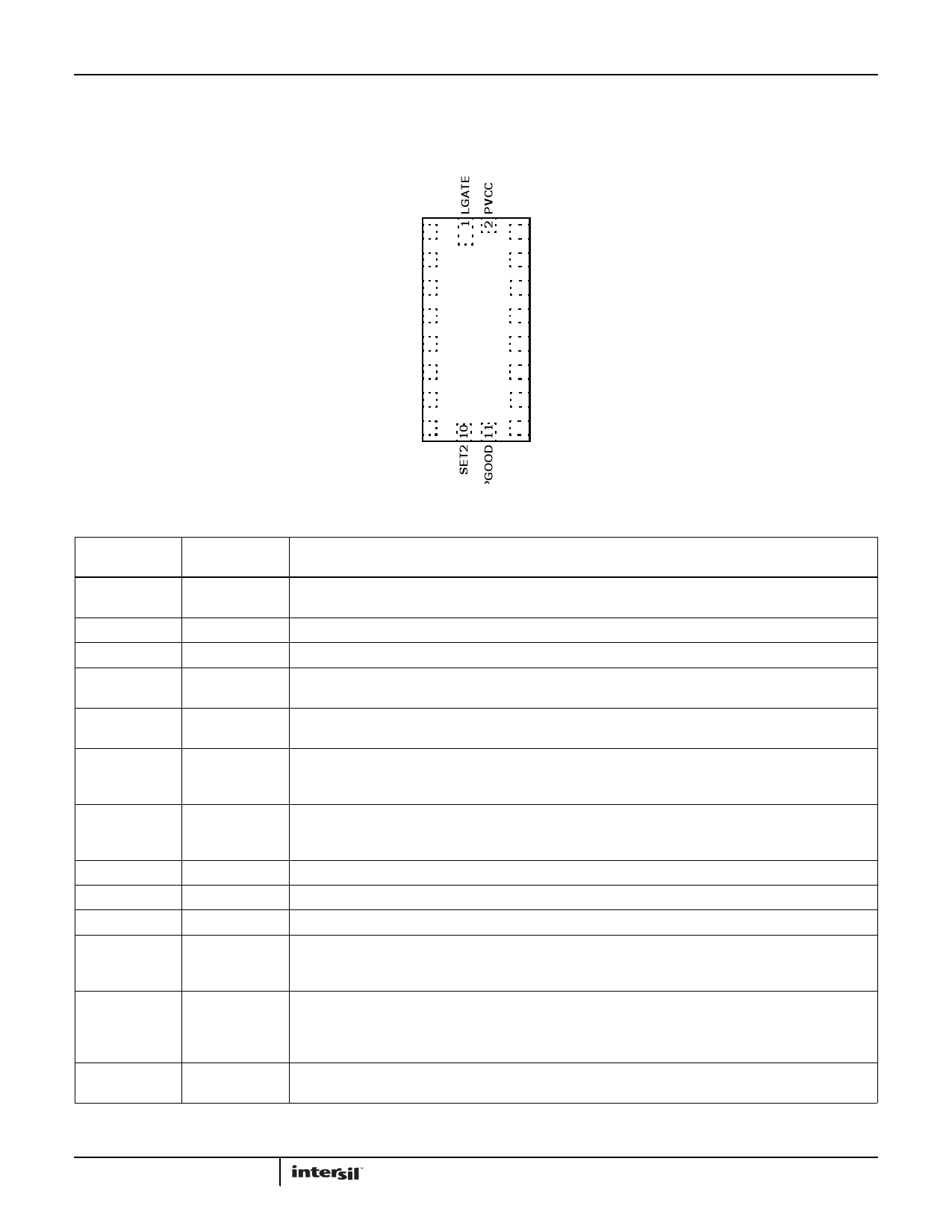
Pin Configuration
ISL62875
ISL62875
(20 LD 3.2X1.8 ΜTQFN)
TOP VIEW
PGND 2
GND 3
EN 4
VID1 5
VID0 6
SREF 7
SET0 8
SET1 9
19 VCC
18 BOOT
17 UGATE
16 PHASE
15 NC
14 OCSET
13 VO
12 FB
ISL62875 Functional Pin Descriptions
PIN
NUMBER
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
SYMBOL
LGATE
PGND
GND
EN
VID1
VID0
SREF
SET0
SET1
SET2
PGOOD
FB
VO
DESCRIPTION
Low-side MOSFET gate driver output. Connect to the gate terminal of the low-side MOSFET of
the converter.
Return current path for the LGATE MOSFET driver. Connect to the source of the low-side MOSFET.
IC ground for bias supply and signal reference.
Enable input for the IC. Pulling EN above the VENTHR rising threshold voltage initializes the
soft-start sequence.
Logic input for setpoint voltage selector. Use in conjunction with the VID0 pin to select among four
setpoint reference voltages.
Logic input for setpoint voltage selector. Use in conjunction with the VID1 pin to select among
four setpoint reference voltages. External reference input when enabled by connecting the
SET0 pin to the VCC pin.
Soft-start and voltage slew-rate programming capacitor input. Setpoint reference voltage
programming resistor input. Connects internally to the inverting input of the VSET voltage
setpoint amplifier.
Voltage set-point programming resistor input.
Voltage set-point programming resistor input.
Voltage set-point programming resistor input.
Power-good open-drain indicator output. This pin changes to high impedance when the
converter is able to supply regulated voltage. The pull-down resistance between the PGOOD
pin and the GND pin identifies which protective fault has shut down the regulator.
Voltage feedback sense input. Connects internally to the inverting input of the control-loop
error amplifier. The converter is in regulation when the voltage at the FB pin equals the voltage
on the SREF pin. The control loop compensation network connects between the FB pin and the
converter output.
Output voltage sense input for the R3 modulator. The VO pin also serves as the reference input
for the overcurrent detection circuit.
5 September 18, 2009
FN6905.1
5 Page 
ISL62875
Theory of Operation
The modulator features Intersil’s R3 Robust-Ripple-
Regulator technology, a hybrid of fixed frequency PWM
control and variable frequency hysteretic control. The
PWM frequency is maintained at 500kHz under static
continuous-conduction-mode operation within the entire
specified envelope of input voltage, output voltage, and
output load. If the application should experience a rising
load transient and/or a falling line transient such that the
output voltage starts to fall, the modulator will extend
the on-time and/or reduce the off-time of the PWM pulse
in progress. Conversely, if the application should
experience a falling load transient and/or a rising line
transient such that the output voltage starts to rise, the
modulator will truncate the on-time and/or extend the
off-time of the PWM pulse in progress. The period and
duty cycle of the ensuing PWM pulses are optimized by
the R3 modulator for the remainder of the transient and
work in concert with the error amplifier VERR to maintain
output voltage regulation. Once the transient has
dissipated and the control loop has recovered, the PWM
frequency returns to the nominal static 500kHz.
Modulator
The R3 modulator synthesizes an AC signal VR, which is
an analog representation of the output inductor ripple
current. The duty-cycle of VR is the result of charge and
discharge current through a ripple capacitor CR. The
current through CR is provided by a transconductance
amplifier gm that measures the input voltage (VIN) at the
PHASE pin and output voltage (VOUT) at the VO pin. The
positive slope of VR can be written as Equation 1:
VRPOS = gm VIN – VOUT CR
(EQ. 1)
The negative slope of VR can be written as Equation 2:
VRNEG = gm VOUT CR
(EQ. 2)
Where, gm is the gain of the transconductance amplifier.
A window voltage VW is referenced with respect to the
error amplifier output voltage VCOMP, creating an
envelope into which the ripple voltage VR is compared.
The amplitude of VW is controlled internally by the IC.
The VR, VCOMP, and VW signals feed into a window
comparator in which VCOMP is the lower threshold
voltage and VW is the higher threshold voltage. Figure 5
shows PWM pulses being generated as VR traverses the
VW and VCOMP thresholds. The PWM switching frequency
is proportional to the slew rates of the positive and
negative slopes of VR; it is inversely proportional to the
voltage between VW and VCOMP.
Synchronous Rectification
A standard DC/DC buck regulator uses a free-wheeling
diode to maintain uninterrupted current conduction
through the output inductor when the high-side MOSFET
switches off for the balance of the PWM switching cycle.
Low conversion efficiency as a result of the conduction
loss of the diode makes this an unattractive option for all
but the lowest current applications. Efficiency is
dramatically improved when the free-wheeling diode is
replaced with a MOSFET that is turned on whenever the
high-side MOSFET is turned off. This modification to the
standard DC/DC buck regulator is referred to as
synchronous rectification, the topology implemented by
the ISL62875 controller.
RIPPLE CAPACITOR VOLTAGE CR WINDOW VOLTAGE VW
ERROR AMPLIFIER VOLTAGE VCOMP
PWM
FIGURE 5. MODULATOR WAVEFORMS DURING LOAD
TRANSIENT
Diode Emulation
The polarity of the output inductor current is defined as
positive when conducting away from the phase node,
and defined as negative when conducting towards the
phase node. The DC component of the inductor current is
positive, but the AC component known as the ripple
current, can be either positive or negative. Should the
sum of the AC and DC components of the inductor
current remain positive for the entire switching period,
the converter is in continuous-conduction-mode (CCM.)
However, if the inductor current becomes negative or
zero, the converter is in discontinuous-conduction-mode
(DCM.)
Unlike the standard DC/DC buck regulator, the
synchronous rectifier can sink current from the output
filter inductor during DCM, reducing the light-load
efficiency with unnecessary conduction loss as the low-
side MOSFET sinks the inductor current. The ISL62875
controller avoids the DCM conduction loss by making the
low-side MOSFET emulate the current-blocking behavior
of a diode. This smart-diode operation called diode-
emulation-mode (DEM) is triggered when the negative
inductor current produces a positive voltage drop across
the rDS(ON) of the low-side MOSFET for eight consecutive
PWM cycles while the LGATE pin is high. The converter
will exit DEM on the next PWM pulse after detecting a
negative voltage across the rDS(ON) of the low-side
MOSFET.
It is characteristic of the R3 architecture for the PWM
switching frequency to decrease while in DCM, increasing
efficiency by reducing unnecessary gate-driver switching
losses. The extent of the frequency reduction is
proportional to the reduction of load current. Upon
entering DEM, the PWM frequency is forced to fall
approximately 30% by forcing a similar increase of the
11 September 18, 2009
FN6905.1
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 22 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet ISL62875.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| ISL62870 | PWM DC/DC Voltage Regulator Controller | Intersil Corporation |
| ISL62871 | PWM DC/DC Controller | Intersil Corporation |
| ISL62872 | PWM DC/DC Controller | Intersil Corporation |
| ISL62873 | PWM DC/DC Controller with VID Inputs | Intersil |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
